In the realm of Natural Language Processing (NLP), the advent of Transformers marked a pivotal shift, fundamentally changing how we approach language understanding and generation. Before Transformers, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) were the primary architecture for handling sequential data like text. This post will explore why Transformers became a game-changer by first understanding the limitations of RNNs.
The Era of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs process input tokens (words) one at a time, maintaining a hidden state that carries information from previous steps. While this sequential processing allows them to build a contextual understanding of a sentence,
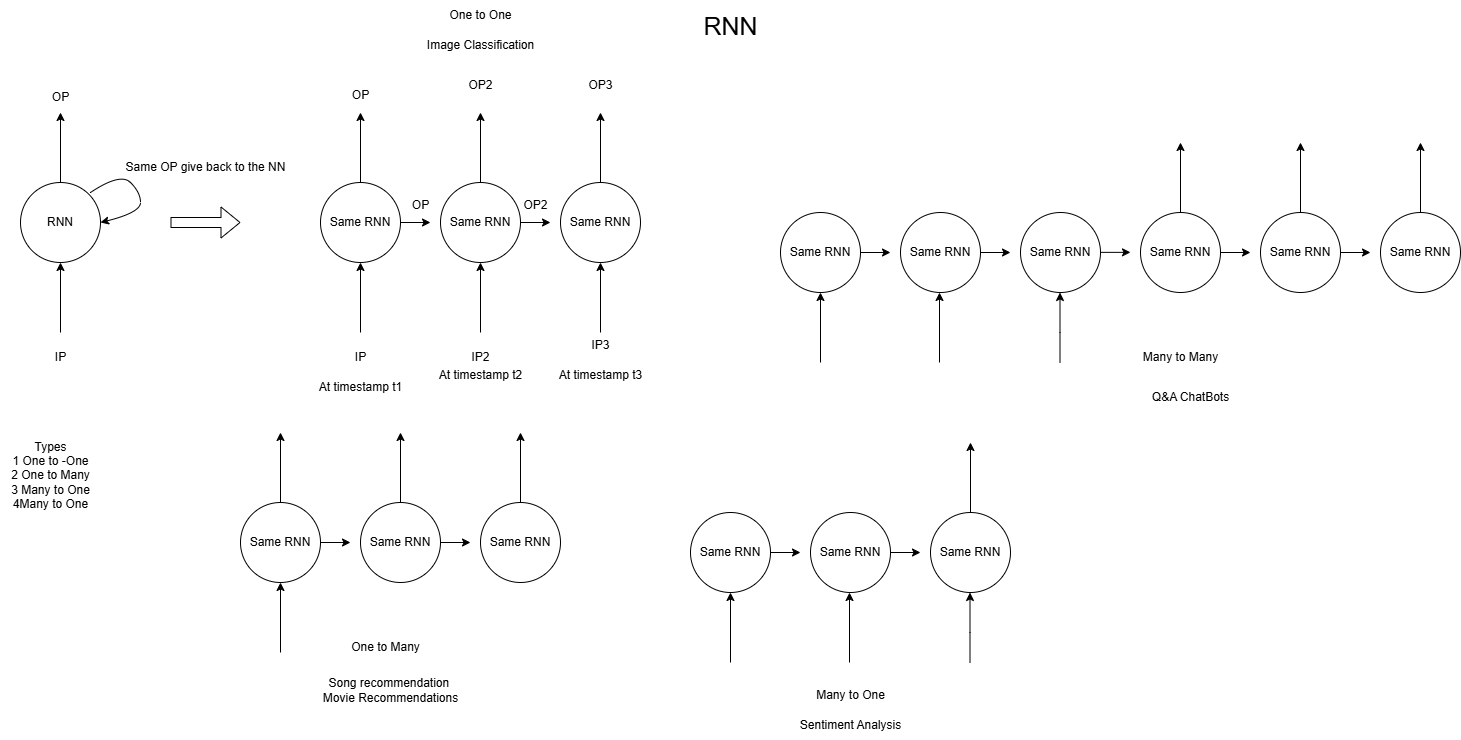
However, this sequential nature presented significant challenges, especially with long sequences. The further apart two related words were, the harder it was for the RNN to maintain their dependency, often leading to issues like the vanishing gradient problem.
The Rise of Transformers
Transformers, introduced in the seminal “Attention Is All You Need” paper, revolutionized NLP by abandoning sequential processing. Instead, they employ a mechanism called self-attention to analyze the entire input sequence simultaneously, processing tokens in parallel rather than step by step.
This parallel processing offers several key advantages:
- Efficiency: It significantly speeds up training, particularly for long sequences.
- Long-range Dependencies: It excels at capturing relationships between words regardless of their distance in the sentence, effectively overcoming the inherent limitations of RNNs.
Self-Attention: Understanding Context
Self-attention enables each word in a sentence to weigh the importance of all other words when computing its own representation. For instance, in the phrase “My Name,” if “My” is represented by a vector [0.1, 0.2, 0.3] and “Name” by [0.11, 0.21, 0.33], these vectors would be spatially close in a multi-dimensional embedding space. This proximity indicates a strong contextual relationship, suggesting they frequently co-occur or are semantically linked within the training data.
Crucially, closeness in vector space doesn’t necessarily imply immediate adjacency in a sentence; rather, it signifies that words share related meanings or roles based on learned patterns.
Conversely, a token like “are” might be represented by [-0.1, -0.7, 0.8]. If visualized, it would occupy a distinct quadrant compared to “My” and “Name,” highlighting a different semantic role.
Feed-forward Neural Network (FFN): Enriching Context
Following the self-attention mechanism, which establishes relationships between words, a Feed-forward Neural Network (FFN) is applied independently to each token. The FFN’s primary role is to enrich the context and sharpen the representation of each token.
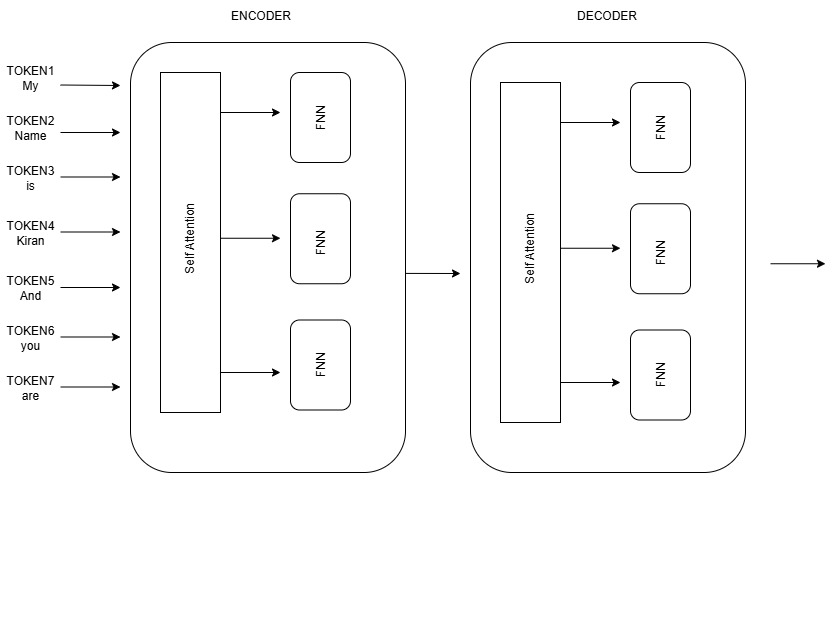 Consider the word “are.” Its meaning is highly context-dependent:
Consider the word “are.” Its meaning is highly context-dependent:
- “Are you going on a walk?” (interrogative)
- “They are late.” (declarative)
After self-attention identifies the overarching relationships, the FFN refines the understanding of which specific meaning of “are” is relevant in the given sentence. In essence, the FFN ensures that post-self-attention, each token’s role is precisely defined and represented for subsequent Transformer layers or the final output.
Conclusion
The Transformer architecture has undeniably transformed the landscape of NLP. By introducing self-attention and parallel processing, it has effectively overcome the inherent limitations of sequential models like RNNs, leading to significantly more efficient training and superior capture of long-range dependencies. This paradigm shift has paved the way for advanced models that power many of today’s state-of-the-art NLP applications, ranging from sophisticated machine translation to highly interactive chatbots.